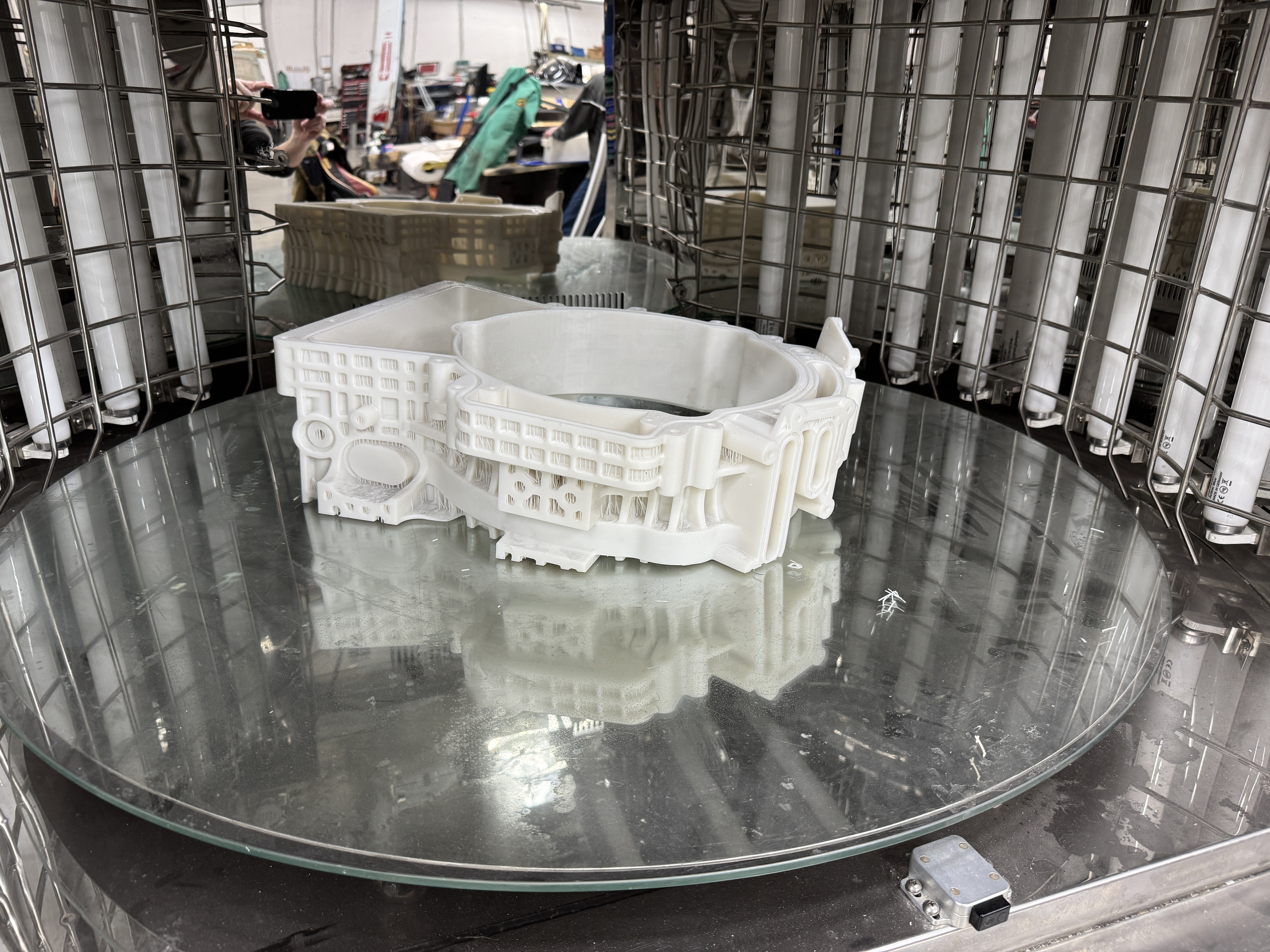
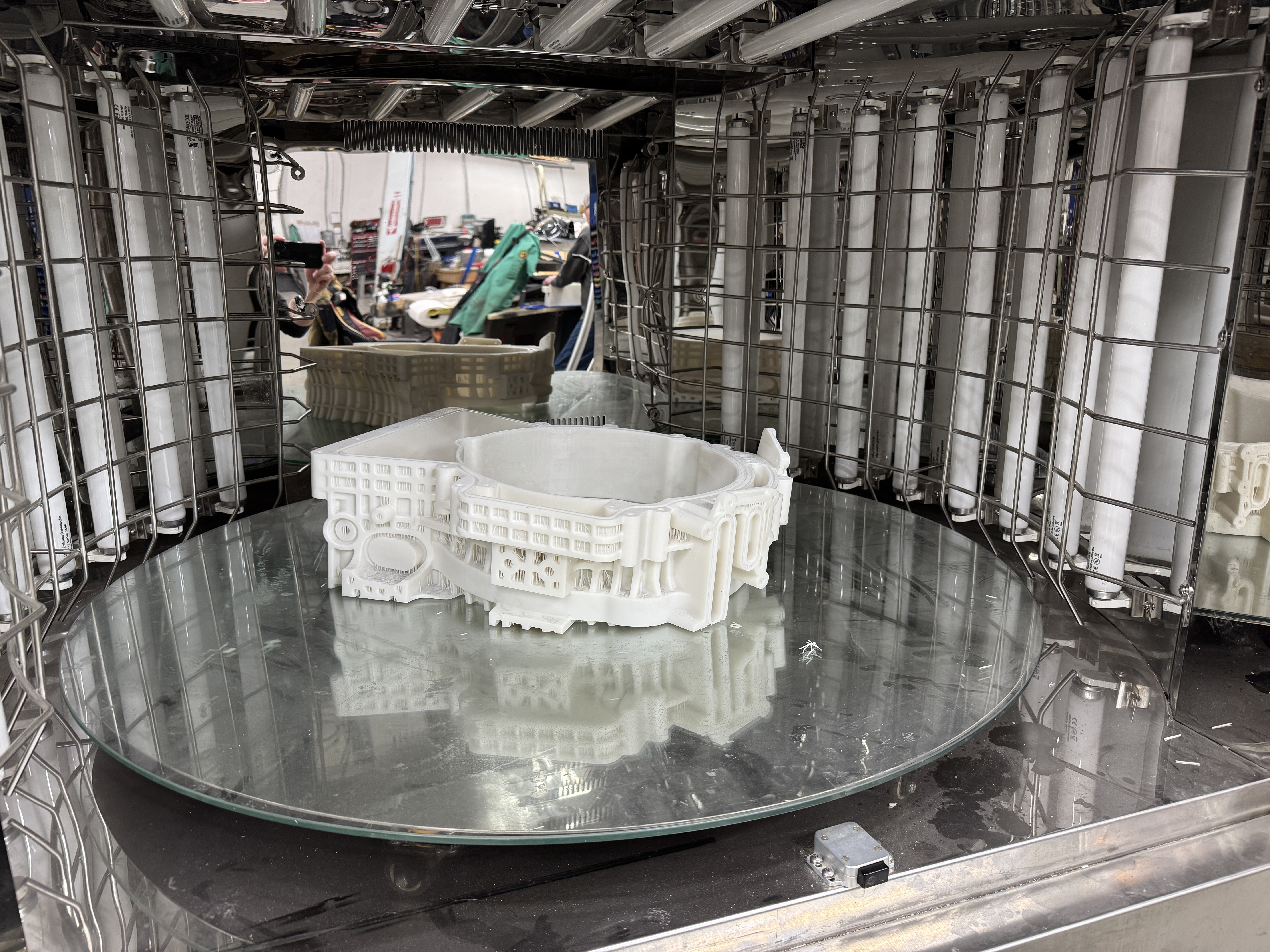
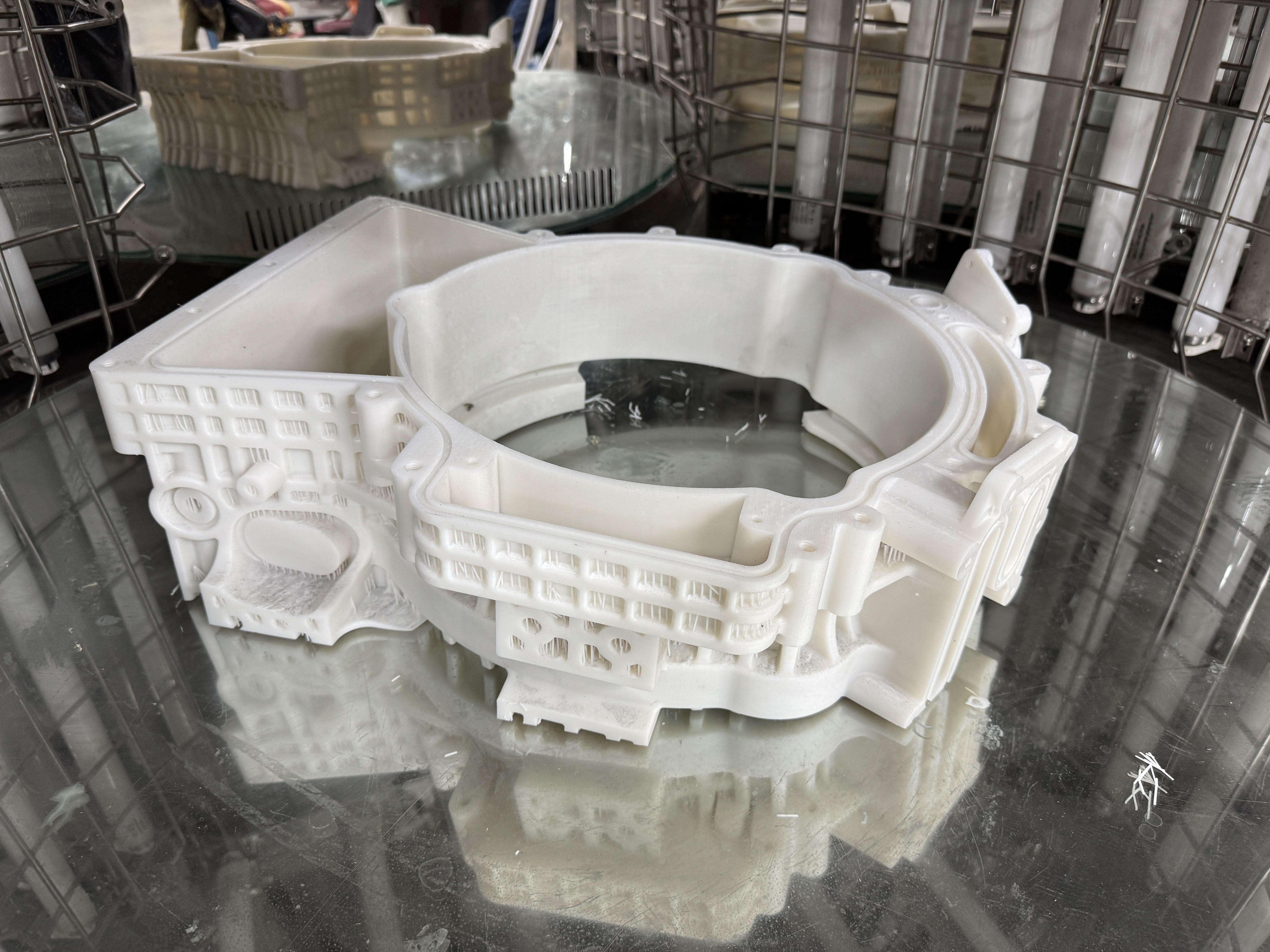
3-D Printing Curing Process
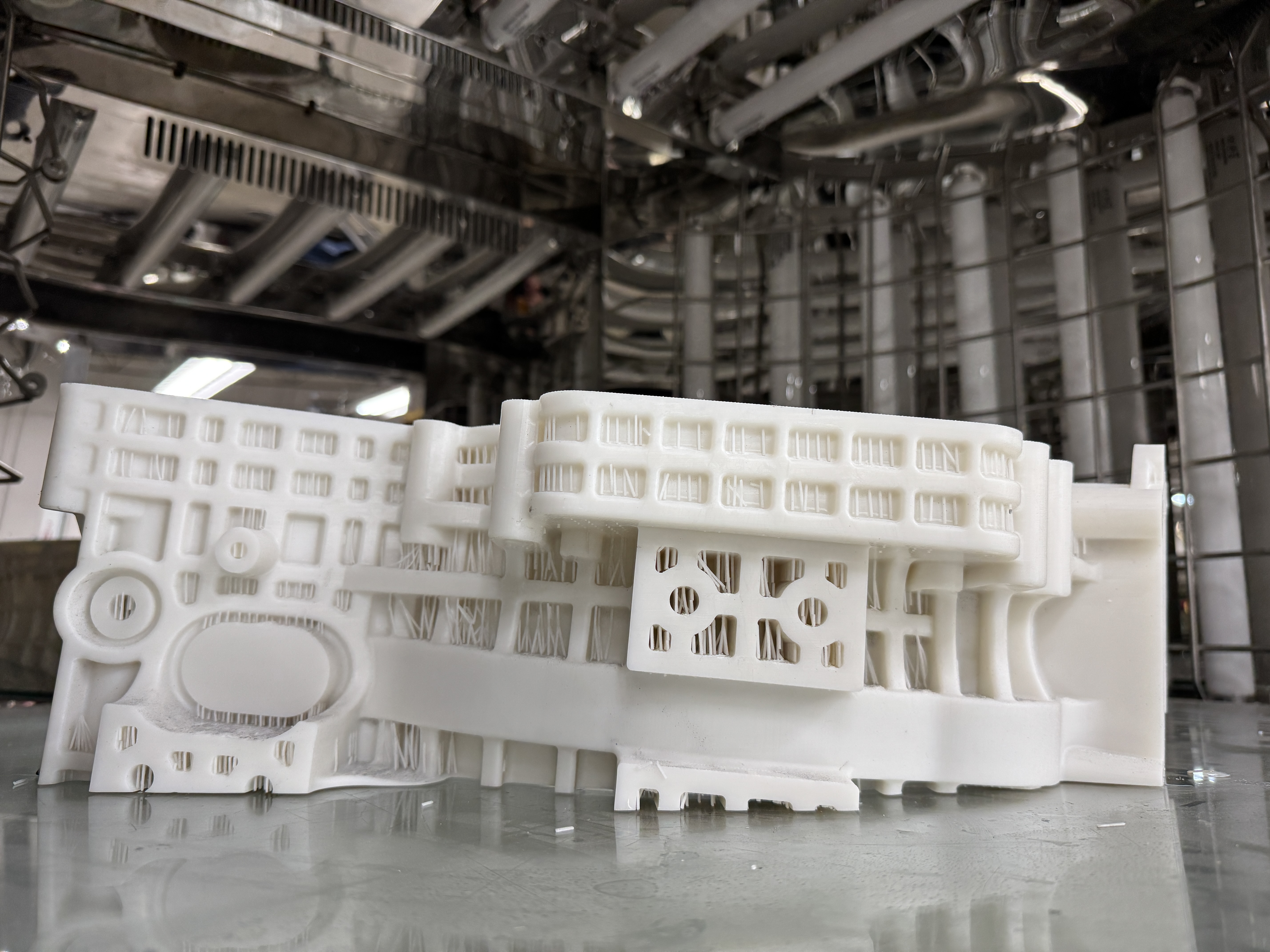
The curing process for large, complex 3D-printed objects is crucial in achieving optimal mechanical properties and structural integrity. This process involves exposing the printed object to UV light and heat to complete the polymerization of the resin.
For large and complex objects, the curing process requires special considerations:
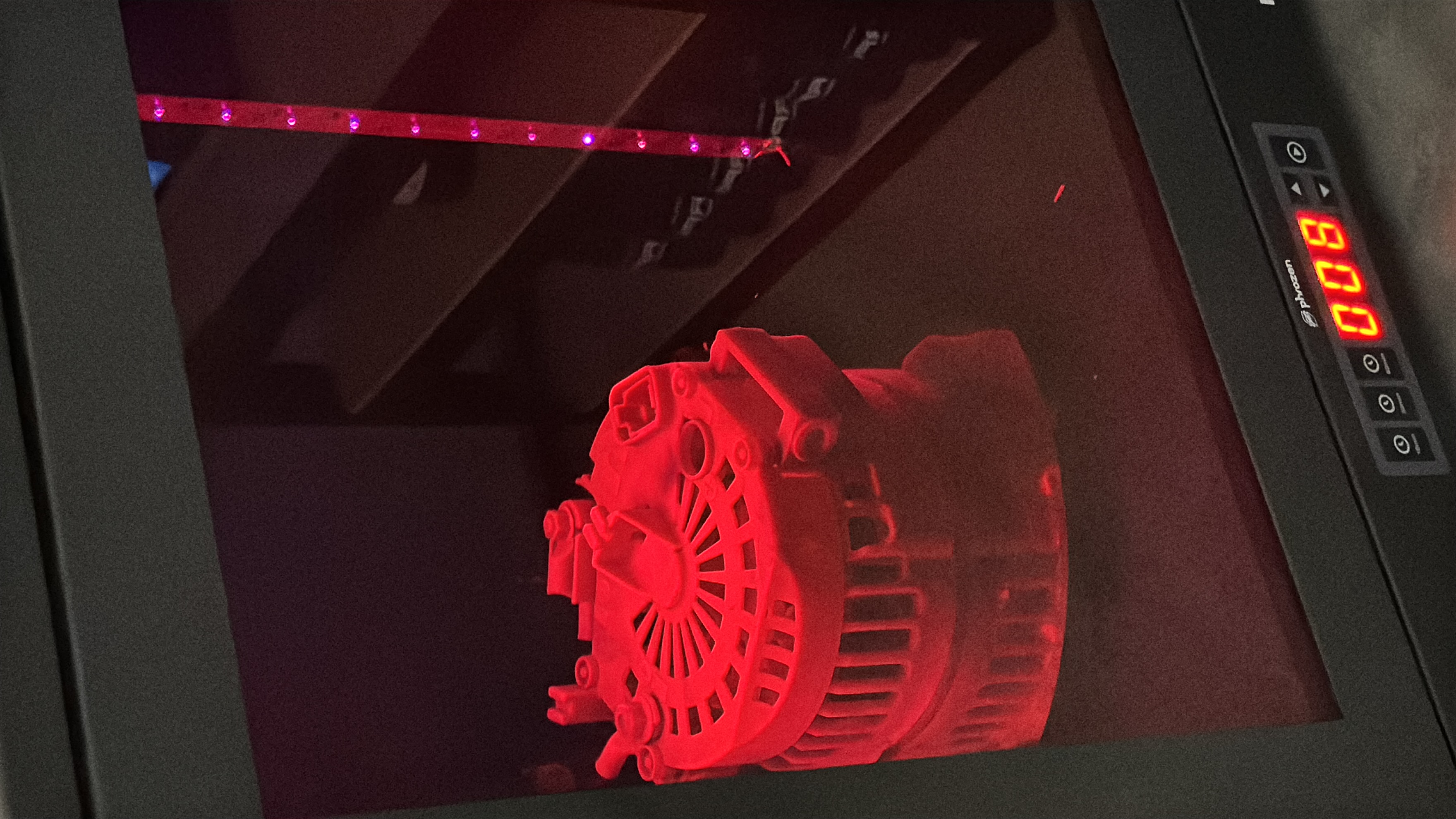
Uniform exposure: Large objects must be rotated during curing to ensure all surfaces receive equal UV exposure. This is often achieved using specialized curing chambers with rotating platforms.
Extended curing times: Larger prints may require up to eight hours to cure fully, compared to smaller objects, which can cure in as little as two hours.
Temperature control: Heat is essential in the curing process, as it increases the mobility of polymer molecules, allowing for more cross-linking6. For large objects, maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the part is crucial.
Penetration depth: UV light may struggle to penetrate deeply into massive or opaque objects. This can result in under-cured internal areas, potentially compromising the object’s overall strength.
Controlled shrinkage: Proper curing helps minimize and control shrinkage, which is particularly important for maintaining the dimensional accuracy of complex geometries.
Post-curing equipment: Large-format post-curing solutions are explicitly designed to curing sizeable 3D-printed parts with precision.
By carefully managing these factors, achieving high-quality, fully cured large and complex 3D-printed objects with optimal mechanical properties and stability is possible.